Ingeniería de Sistemas y Autmática
Vector Control of AC Drives. Details
Control of multiple motors from
a single inverter
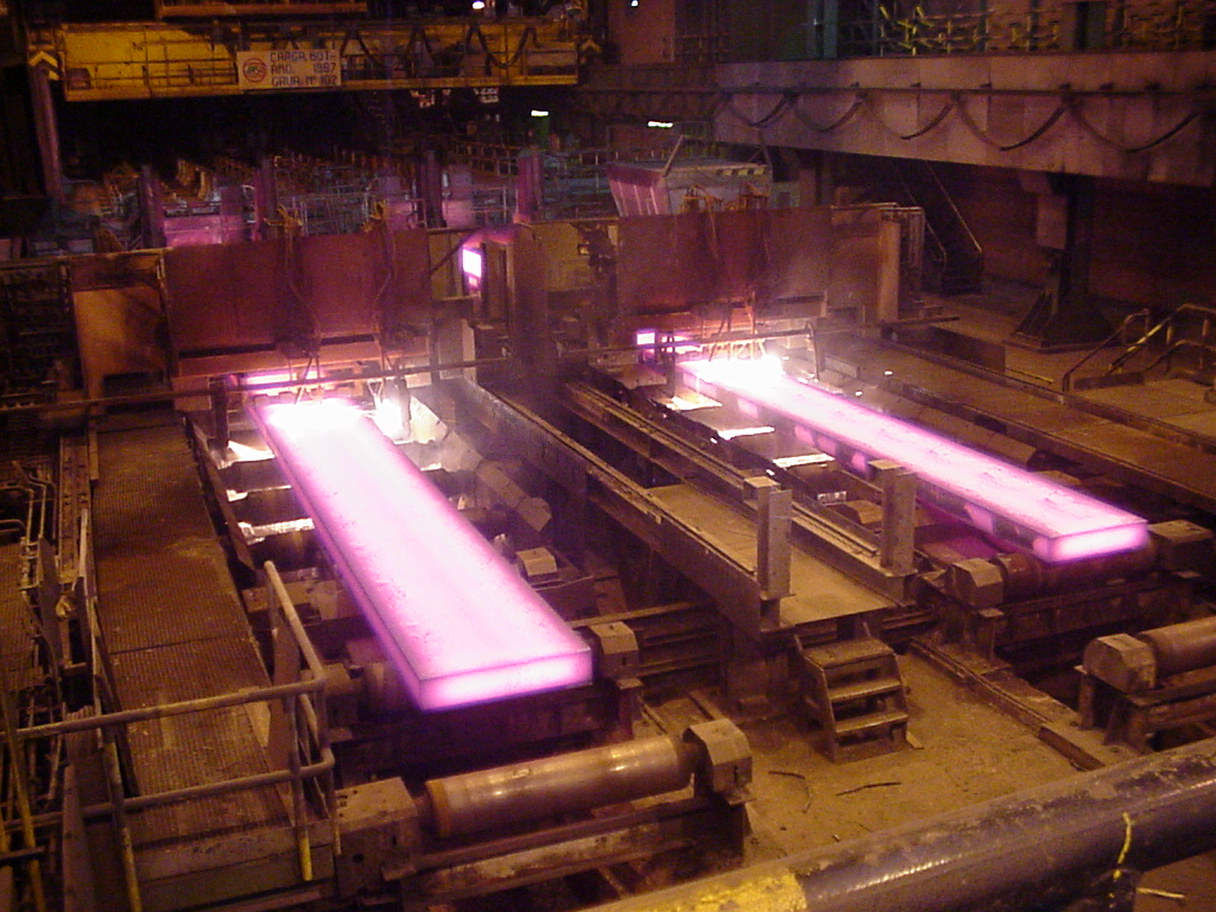
Control of several motors from a single inverter and with a reduced
number of sensors is often found in the strands in rolling mills, as shown
in Figure 2-left. The utilisation of an inverter for each motor is not
a solution because of the increase in the final cost, the added complexity
in the hardware what also results in a decreased reliability, additional
cabling, etc. AC drives installed in such applications work based on a
volts/Hz control, with the limitation in the performance intrinsic to this
technique. The goal of this project was to obtain performances closer to
field oriented controlled AC drives without adding any additional hardware.
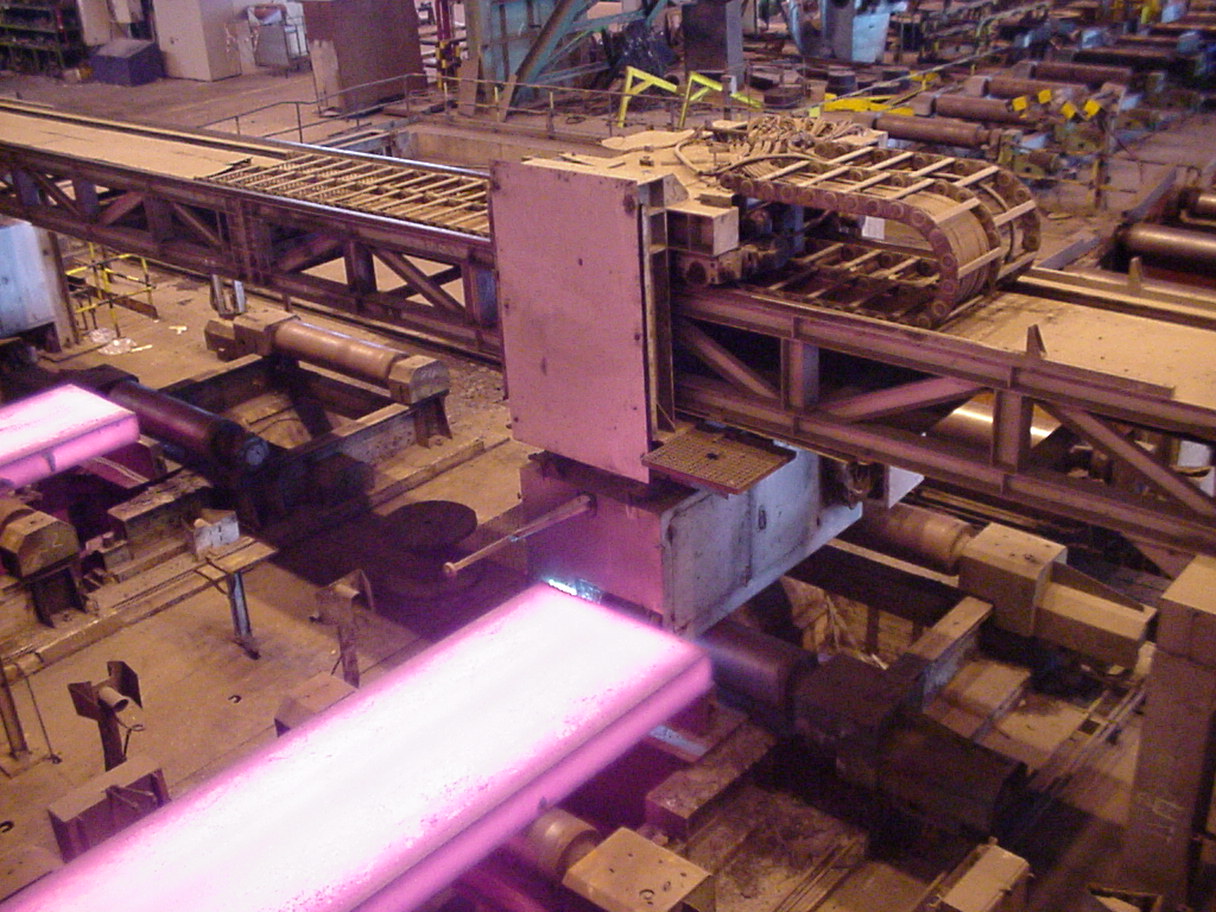
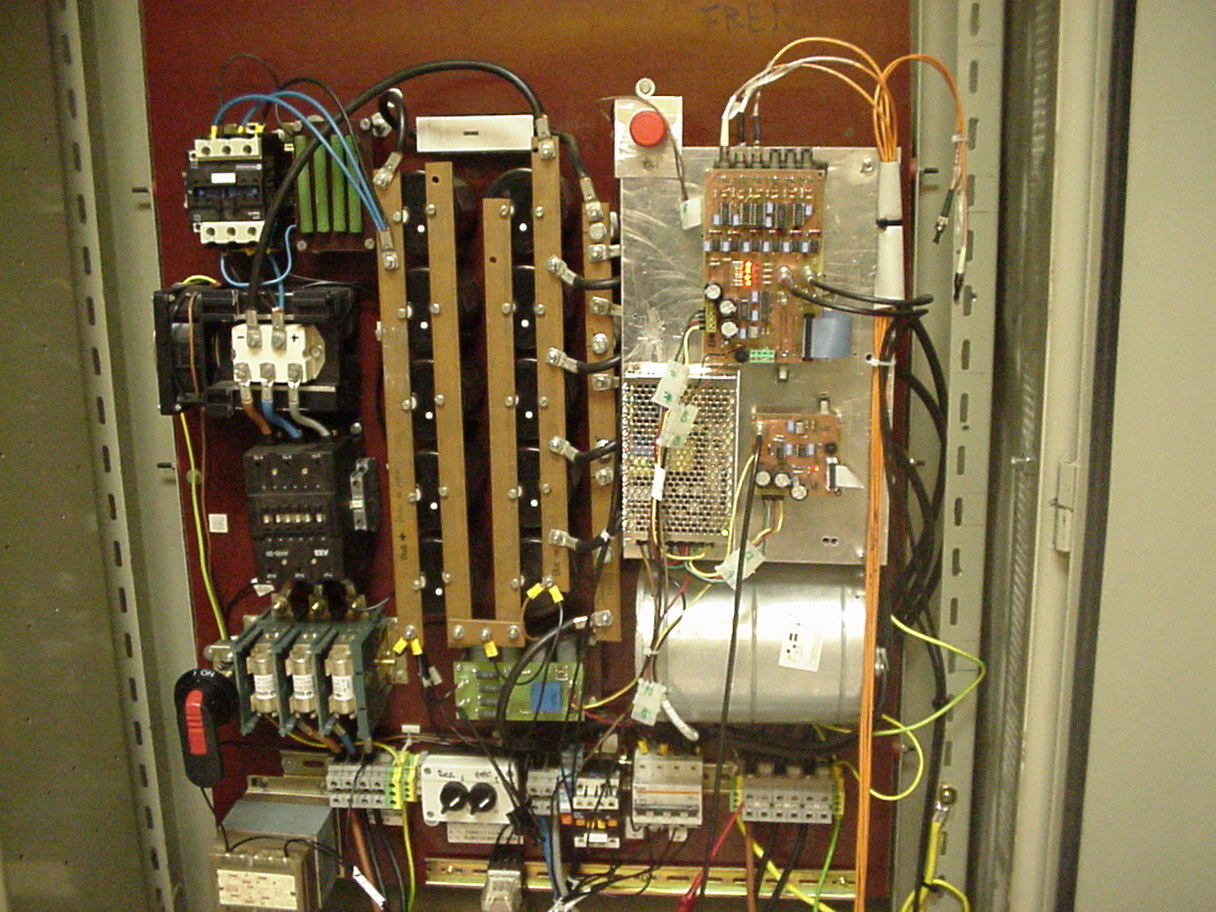
The inverter developed for this project is shown in Figure 2-right, the
control stage being based on a TMS320C30, a 32 bits, floating point DSP
by Texas Instruments.

|
|
Figure 2: Left: Partial view of the strand.
Right: View of an AC drive prototype developed for the control of a rolling
desk, consisting of six induction motors fed from a single inverter. It
includes a three phase inverter Skiip module by Semikron.
Surface defects in the slabs are for instance introduced during the
cutting process (Figure 3-left). These defects will produce an unbalanced
torque distribution among the motors of the desk. Volts/Hz controlled drives
operating the rolling desk previous to the stamping machine (Figure 3-right)
are unable to keep the slab at stand still during the stamping process.
A field oriented controlled drive succeeded implementing an effective position
control for such application.
Figure 3: Left: Cutting process. Right: Stamping
machine.
Carrier injection based sensorless
control
In its most common implementation, field oriented control of ac machines
produces torque by injecting the torque producing component of the stator
current so that it is always orthogonal to the rotor flux in the machine.
To implement this class of field oriented controller knowledge of the rotor
flux position is necessary. For full range operation of field oriented
machines, rotor flux position is generally estimated using rotor position
measurement. In addition to this, the measurement or estimation of position
and/or velocity will be necessary for motion control.
The estimation of flux, position and velocity using the terminal properties
of the motor (voltages and/or currents) has been a very active area of
research for the last years, the reason being the cost and reliability
problems associated with the mechanical sensors (usually encoders and resolvers)
and cabling. The techniques proposed so far to accomplish this goal can
be categorised in two major groups:
-
Techniques based on tracking the back-emf.
-
Techniques based on tracking of spatial saliencies (asymmetries).
Despite of being more popular, techniques based on tracking the back-emf
present a major limitation, since the back-emf is the effect of a revolving
field, they can not work at very low or zero speed.
Techniques based on tracking saliencies can potentially be used to estimate
both the flux of the rotor position. A potential implementation of these
techniques is shown in Figure 4. A high frequency carrier voltage (several
hundred Hertz) is injected to the motor in addition to the fundamental
voltage. The induced high frequency current will contain information relative
to the position of saliencies (asymmetries) present in the motor. This
information is extracted by means of some advanced digital filtering. The
major advantage of this technique is that it doesnít depend on the fundamental
excitation, providing a wide bandwidth estimation even at low or zero speed.

Figure 4: Injection of a Carrier Signal Voltage
Excitation for the Estimation of Rotor Position or Flux Angle
Saliencies are intrinsic to any motor design (e.g. due rotor and stator
slotting). They are also produced due to the saturation of the flux paths,
what can be used to estimate the main flux position. Rotor position dependent
saliencies can also be introduced during the machine design or in a further
modification to provide position feedback. An example of this is shown
in Figure 5. The rotor slots are opened following a sinusoidal modulation,
the induced carrier current containing information about the position of
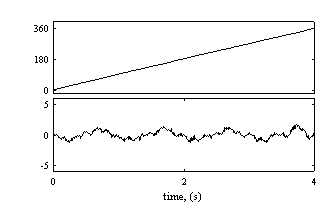
the saliency, and therefore of the rotor. Figure 6. shows the estimated
position and the estimation error using this technique.
Figure 5: Rotor of a 0.75 kW induction machine
modified to create a spatial dependent saliency by opening the rotor slots
|
(Mech.Deg.)
|
|
|
Error (Mech.Deg.)
|
Figure 6: Estimated Rotor Position and Estimated
Rotor Position Error
Publications in International Conferences
-
A. Diez, J.A. Cancelas, F. Mateos, J.A. Sirgo, F. Briz, "Design of Speed
Digital Interface to ac Drives", Mediterranean Electrotechnical Conference
MELECON, Ljubljana, Yugoslavia, May 1991, pp: 1281-1284, ISBN 0-87942-655-1
-
F. Briz, J.A. Cancelas, A. Diez, J. Gomez, "Design of ac Drives with Position
and Speed Dynamic Control", Workshop Motion Control for Intelligence Automation
(IFAC), Perugia, Italy, October 1992, pp: 159-163
-
F. Briz, J.A. Cancelas, A. Diez, "Design of ac Drives with Position and
Speed Dynamic Control Using DSP", Internation Power Electronics Congress,
CIEP, Cuernavaca, Mexico, August 1993, pp: 95-100, ISBN: 0-7803-1405-0
-
F. Briz, J.A. Cancelas, A. Diez, "Speed Measurement Using Rotary Encoders
for High Performance ac Drives", International Conference on Industrial
Electronics, Control and Instrumentation IECON, Bolognia, Italia, September
1994, pp: 538-542, ISBN: 0-7803-1328-3
-
F. Briz, F;J.C. Alvarez, A Diez, "Speed Estimation Using Torque Observer
in FOC Systems", Workshop Motion Control (IFAC), Munich, Germany, October
1995, pp: 67-74
-
Fernando Briz, M.W. Degner, R.D. Lorenz, "Analysis and Design of Current
Regulators Using Complex Vectors", IEEE Industry Applications Society Annual
Meeting, New Orleans, USA, October 1997, pp: 1504-1511, ISBN: 0-7803-4067-1
-
Fernando Briz, A. Diez, M.W. Degner, R.D. Lorenz, "Current and Flux Regulation
in Field Weakening Operation", IEEE Industry Applications Society Annual
Meeting, Saint Louis, USA, October 1998, pp: 524-531, ISBN: 0-7803-4943-1
-
Fernando Briz, M.W. Degner, R.D. Lorenz, "Dynamic Analysis of Current Regulators
for AC Motors Using Complex Vectors", IEEE Industry Applications Society
Annual Meeting, Saint Louis, USA, October 1998, pp: 1253-1260, ISBN: 0-7803-4943-1
-
L.A. de Souza, M.W. Degner, Fernando Briz, R.D. Lorenz, "Compensating Carrier
Frequency Current and Voltage Injection for the Estimation of Flux, Position
and Velocity in Sensorless AC Drives", IEEE Industry Applications Society
Annual Meeting, Saint Louis, USA, October 1998, pp: 452-459, ISBN: 0-7803-4943-1
-
F. Cabanas M, G. Melero M., A. Orcajo G., Fernando Briz, Capolino G.A.,
"A New Methodology for Applying the FFT to Induction Motor On-Line Diagnosis",
IEEE International Symposium on Diagnostics for Electrical Machines, Power
Electronics and Drives, Gijón, Spain, September 1999, pp: 537-544,
ISBN: 84-699-0977-0
-
L.A. de Souza, M.W. Degner, Fernando Briz, R.D. Lorenz, "Using Carrier
Frequency Current Injection for the Estimation of Flux, Position and Velocity
Drives", 5th Brazilian Power Electronics Conference COBEPí99,
Brazil, September 1999, pp: 673-680
-
Fernando Briz, A. Diez, M.W. Degner, "Dynamic Operation of Carrier Based,
Sensorless, Direct Field Oriented AC Drives", IEEE Industry Applications
Society Annual Meeting, Phoenix, USA, October 1999, pp: 2313-2320, ISBN:
0-7803-5589-X
-
Ignacio Díaz Blanco, Alberto B. Diez González, Abel A. Cuadrado
Vega, José M. Enguita González, "RBF Approach for Trajectory
Interpolaton in Self Organizing Map based Condition Monitoring", Emerging
Technologies and Factory Automation ETFA'99, (UPC, Bacelona), October 18-21,
1999
-
J.M. Guerrero, Fernando Briz, A. B. Diez, J.C Alvarez, "Design and Tuning
of PI Velocity Regulators for High Performance AC Drives", IFAC Workshop
on Digital Control PIDí00, Terrassa, Spain, April 2000, pp: 107-112
-
Fernando Briz, A. Diez, M.W. Degner, R.D. Lorenz, "Measuring, Modeling
and Decoupling of Saturation Induced Saliencies in Sensorless, Vector Controlled,
AC Drives", IEEE Industry Applications Society Annual Meeting, (to be held
in Rome, Italy in October 2000).
Publications in International Journals
-
Fernando Briz, Michael W. Degner, Robert D. Lorenz, "Dynamic Analysis of
Current Regulators for AC Motors Using Complex Vectors", Transactions on
Industry Applications, Vol. 35, nº 6. Nov./Dec. 1999, pp.1413-1424,
ISSN: 0093-9994
-
Fernando Briz, Michael W. Degner, Robert D. Lorenz, "Analysis and Design
of Current Regulators Using Complex Vectors", Transactions on Industry
Applications, Vol. 36, nº 3, May/June 2000, ISSN: 0093-9994
-
Fernando Briz, Alberto B. Diez, Michael W. Degner, "Dynamic Operation of
Carrier Signal Injection Based, Sensorless, Direct Field Controlled AC
Drives", to be published in the Transactions on Industry Applications,
Vol. 36, nº 5. Sept./Oct. 2000, ISSN: 0093-9994
-
Fernando Briz, Alberto B. Diez, Michael W. Degner, R. D. Lorenz, "Current
and Flux Regulation in Field Weakening Operation", accepted for its publication
in the Transactions on Industry Applications, ISSN: 0093-9994
Main Research Groups









